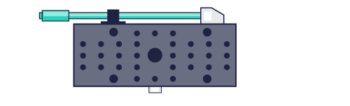
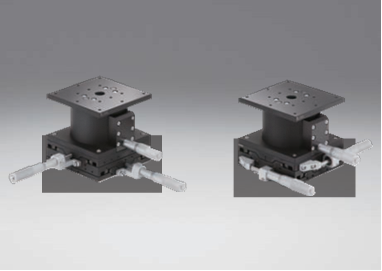
Ultra thin steel stages (10mm) provide high stiffness and load capacity in a very low profile. Stage heights are 40% lower and the overall weight is 35% lighter than standard TSD stages. (TSDH)
- Opposed locking clamp to maximize locking
- Low-profile is ideal for assembling into systems with limited space or optical applications that require low beam
Hardened steel linear stages with integrated bearing ways and a black chrome finish. Our “Extended Contact” technology yields superior stability, stiffness, accuracy, and durability. These XY stages are integrated and therefore have a lower profile vs. (2) single axis stages combined (TSDS).
There are options for micrometer position and fine pitch screws.
Aluminum translation stage with high stiffness bearing ways. Cost effective and light weight. (TADC)
- Unique steel bearing ways with 4-point extended contact yield stable load capacity in all
- Long life, maintenance free.
Linear stages based on extended contact ball bearing guide which provides high precision, load capacity, stiffness and durability. Available in 15, 25, 40, 60, 65, 80, 100, 120 mm square stage sizes and others on request.
High Load Capacity and High Stiffness
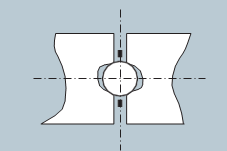
The four-array contact structure achieves high load capacity and high stiffness (13 times stiffer than the V groove).
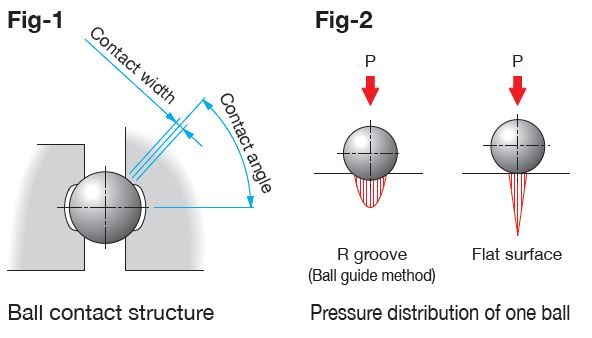
As shown in Fig-1, ball guides are machined across the arcs so that they have R groove structure and good contact with a ball allowing stable load capacity against the load in the directions where contact with the ball occurs frequently.
High Durability
Long life and free of maintenance
Fig-2 shows the pressure distribution of the R groove and the flat surface. As shown in the figure, pressure exerted on the R groove is dispersed and does not reach inside. Thus, metal fatigue and wear are reduced.
High Precision
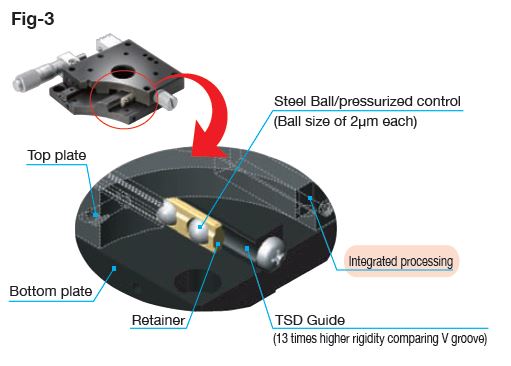
The integral (simultaneous) machining achieves high precision (straightness: 0.7 μm or lower)
As shown in Fig-3, the top and bottom plates are integrally and simultaneously machined using an originally devised machining jig to minimize respective machining errors. That is, to maintain high precision, these plates are machined in virtually the same state as when a ball is inside.
Low Profile
Reduction in the number of parts enables low profiling
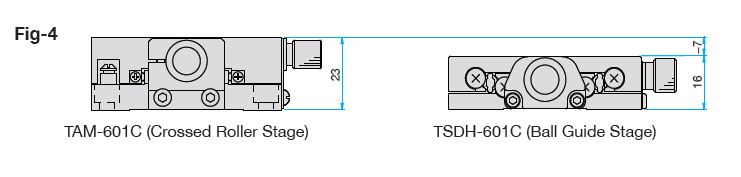
Fig-4 shows a comparison of thickness of a crossed roller stage and a ball guide stage. The integration of the guides into the top and bottom plates allows low profiling of the ball guide stage virtually the same state as when a ball is inside.