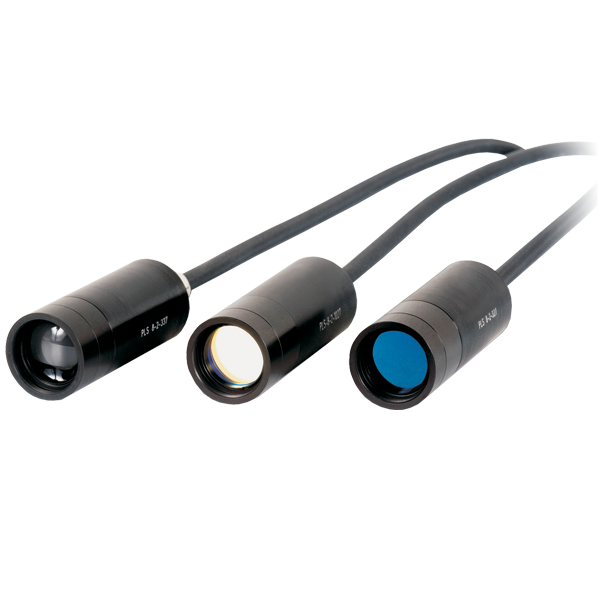
Picosecond pulsed LEDs
- Wavelengths from 255 to 600 nm
- Peak power up to 2.5 mW
- Pulse widths as short as 600 ps (FWHM)
- Repetition rate from single shot up to 40 MHz
- Optional bandpass filter
The pulsed LEDs of the PLS Series are the fastest miniature sub-nanosecond pulsed LED sources commercially available. They combine short pulse widths with high repetition rates in a compact and maintenance free set-up.
Direct emission in the ultraviolet
The LEDs of the PLS Series are the only available compact pulsed light sources that emit directly in the ultraviolet spectral range at wavelengths as short as 255 nm. Eight different LEDs with central wavelengths between 255 nm and 370 nm allow to choose a peak wavelength according to the needs of the application. Their spectral and timing characteristics are also particularly suitable for biomedical applications, e.g., for the detection of labeled substances as well as naturally fluorescent amino acids like tryptophan or tyrosine.
Pulse widths down to 600 ps
All pulsed LEDs emit picosecond pulses with a full width at half maximum (FWHM) of less than one nanosecond – at some wavelengths even pulse widths down to 600 ps are possible. The pulse width itself cannot be controlled, but does depend on the selected power level of the LED.
Average power of several microwatts
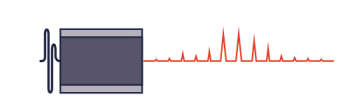
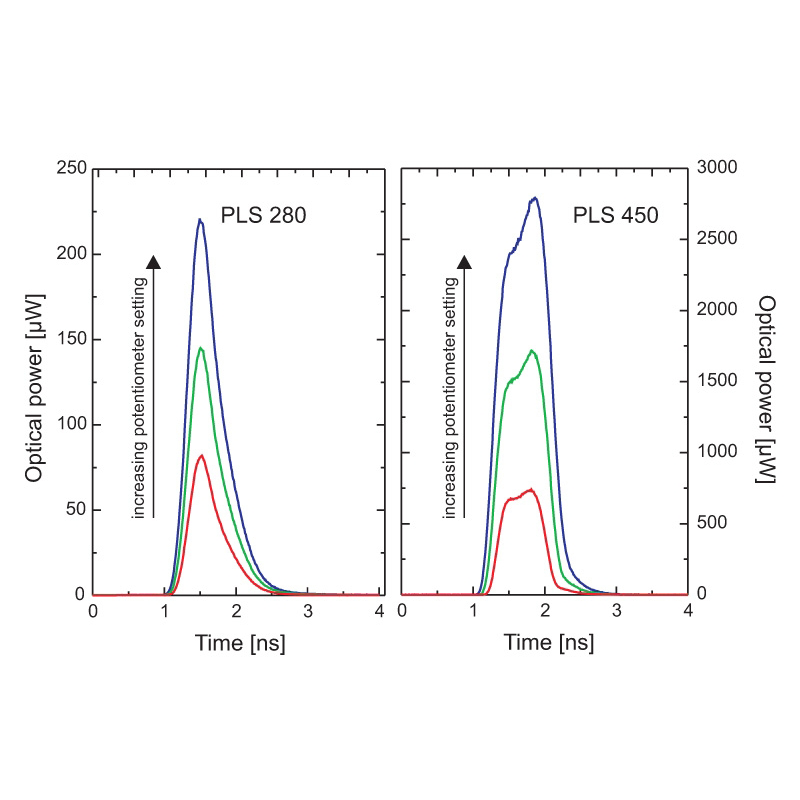
Pulse profile examples of the PLS Series pulsed LEDsAll LED heads are designed to emit an about constant pulse energy at a given intensity setting. Doubling the repetition rate therefore effectively doubles the average output power. The achievable pulse energies of the LEDs in the visible spectrum can reach up to 2 pJ, which corresponds to average output powers up to 80 µW at 40 MHz repetition rate. For the UV LEDs the achievable pulse energy is lower and typically below 1 pJ. At their maximum repetition rate of 10 MHz, this corresponds to average output powers around 1 µW.
Spectral width down to 10 nm
The spectral emission profile of all pulsed LEDs is broader than for pulsed diode lasers. For the UV LEDs the spectral width is smaller than 20 nm, whereas for the LEDs in the visible it may be as large as 50 nm. A further reduction of the spectral width is possible by using suited bandpass filters.
Suitable for time-resolved fluorescence spectrometers
The most important difference between the pulsed LEDs and pulsed diode lasers is the fact that the emission of the LEDs is divergent, not coherent, not polarized and also non-uniform in its intensity distribution. Depending on the LED used, different beam shapes can be seen ranging from near-round to elliptical. Fiber coupling into single mode or multimode optical fibers has therefore only very low efficiency – a notable exception are large area fibers such as liquid light guides. However, for short range interactions, e.g., in a compact time-resolved fluorescence lifetime spectrometer the LEDs of the PLS Series are very useful excitation sources.
All functions of the PLS Series LED heads such as repetition rate and output power are controlled and adjusted by any driver of the PDL Series.